Long production times, defective products, and costly machine maintenance are just a few of the many challenges facing manufacturing companies today. However, with the implementation of data-driven artificial intelligence (AI), the manufacturing industry is entering a new era.
AI technology is no longer limited to large manufacturers. Many valuable and cost-effective AI solutions are now available, helping to reduce costs, improve product quality, and minimize downtime.
AI is a perfect fit for the manufacturing industry, as it involves producing many identical parts and products. Manufacturing generates vast amounts of data that can be harnessed by AI algorithms to identify issues or optimize processes.
According to a World Economic Forum survey of international manufacturers, 89% of companies plan to deploy AI in their manufacturing networks soon, while 68% have already begun implementing AI solutions. Additionally, Capgemini’s research shows that 44% of organizations in the manufacturing sector are currently utilizing artificial intelligence prototypes.
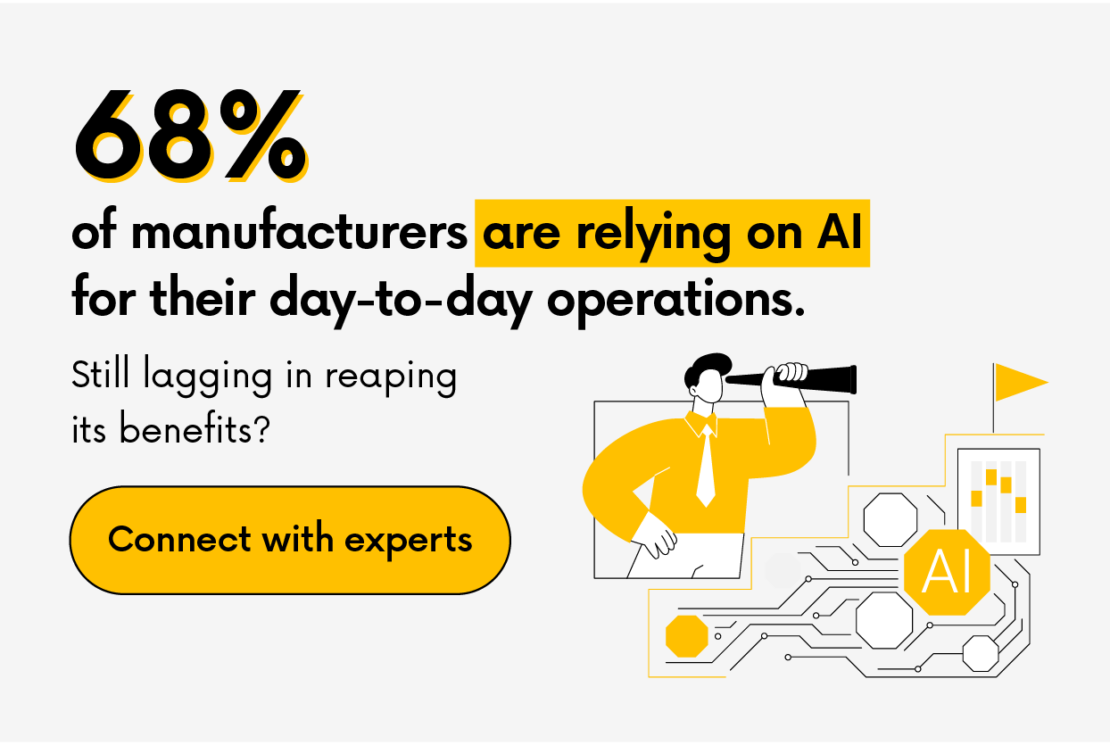
Table of Contents
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a set of mathematical algorithms that learn patterns to simulate human thinking. The scope of AI includes neural networks, robotics, and the creation of intelligent models of behavior. These systems can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
Today’s AI capabilities include speech, image, and video recognition; autonomous object creation; natural language processing; intelligent automation; advanced simulation; and complex analysis and prediction.
In the context of manufacturing operations, most AI use cases revolve around the following technologies:
1. Machine Learning: The ability of algorithms and software to analyze data and automatically learn from patterns without being explicitly programmed.
2. Deep Learning: An advanced form of machine learning (requiring large amounts of data) that uses artificial neural networks to analyze and interpret images and videos.
3 Autonomous Objects: Artificial agents, such as collaborative robots or autonomous vehicles, that can independently perform tasks assigned to them.
How Is Artificial Intelligence Currently Being Used in the Manufacturing Sector?
According to a Deloitte survey, 27% of companies believe that AI projects have already brought value to their operations, and 56% expect these projects to deliver value within 2–5 years. This demonstrates the significant potential of AI in reducing critical errors, catching product defects, improving planning, and enhancing safety measures.
What once seemed like a futuristic vision—factories filled with robots—has become a reality today. Autonomous robots now interact with each other and learn from their human counterparts. Computers are trained to detect even the smallest defects in machines and products, and the combination of artificial intelligence with IoT devices enables predictive maintenance, significantly improving equipment performance evaluation.

Many prominent manufacturers are already leveraging AI to optimize their processes. For example, Danone uses machine learning to predict demand variability and enhance planning. This feature has improved the forecasting process, leading to better coordination between departments like marketing and sales. As a result, Danone achieved a 20% reduction in forecast errors and a 30% decrease in lost sales.
Similarly, General Motors has introduced a machine learning system called “Dreamcatcher” to revolutionize prototyping. The system was recently used to prototype parts of a seatbelt support, resulting in a one-piece design that is 40% lighter and 20% stronger than the original eight-piece version.
Manufacturers can benefit from AI implementations in a variety of ways. Below, we will explore some examples of AI applications in manufacturing that are worth considering for your business.
Current Trends in the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing
1. Predictive Maintenance and Equipment Monitoring
One of the most impactful applications of AI in manufacturing is predictive maintenance. By analyzing IoT sensor data and monitoring machine performance in real time, AI algorithms can predict when equipment requires maintenance. This allows manufacturers to make timely repairs, preventing unexpected failures that could lead to costly downtime.
Smart maintenance provides several key benefits, including:
- Recommending the optimal time for maintenance based on the equipment’s current condition.
- Analyzing root causes and identifying factors contributing to machine downtime, helping prevent future failures.
- Evaluating the impact of issues on machine performance and overall failures.
- Minimizing production losses and enhancing overall equipment efficiency.
- Providing the “right alerts at the right time ” is essential for avoiding excessive false alerts—a common pitfall with many smart maintenance systems.
2. Optimizing Supply Chains
AI’s ability to quickly process large volumes of data makes it a powerful tool for supply chain optimization. By leveraging AI, manufacturers can reduce inventory costs, minimize waste, and increase supply chain resilience, helping them better manage global disruptions such as pandemics or geopolitical events.
In the context of supply chain optimization, AI can:
- Uncover hidden patterns and relationships in large datasets that help manage logistics networks, including cargo ships, delivery trucks, warehouses, and distribution centers.
- Track physical goods each time they change hands.
- Forecast production capacity and optimize storage based on customer demand.
- Signal potential delays and equipment failures before they create production bottlenecks.
- Draw insights from the vast streams of data generated by IoT sensors embedded in warehouse and transportation infrastructure.
3. AI-Powered Automation and Robotics
Automation has long been integral to manufacturing, but AI is taking it to the next level. Currently, it takes highly paid engineers about two weeks to optimize robots so they can perform at their full potential. Unlike traditional robots, which require extensive programming, AI-powered robots can learn from their environment and adjust their actions in real time.
With preloaded patterns as a foundation, these AI robots are capable of handling complex tasks like quality control, assembly, and material handling with minimal human intervention. AI-driven automation not only increases productivity but also enhances safety by reducing human involvement in hazardous or repetitive tasks.
4. AI-Assisted Quality Control
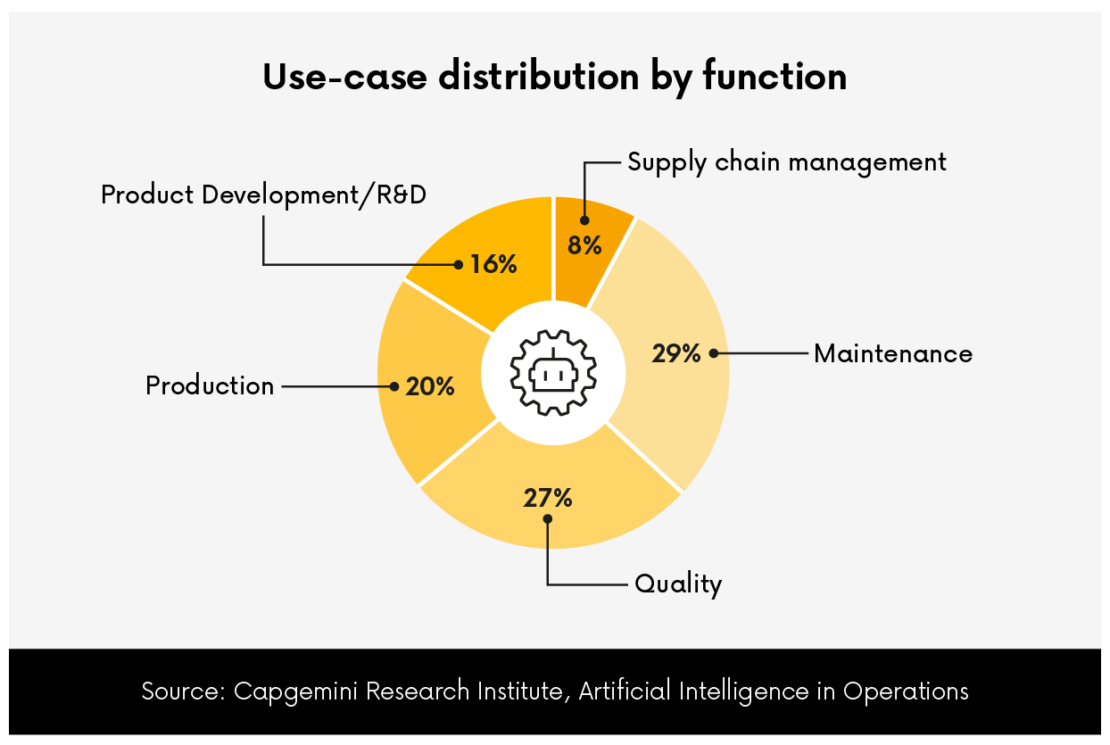
Ensuring product quality is vital in manufacturing, and AI plays a crucial role in this domain. While AI offers significant potential across the manufacturing sector, the greatest efforts are concentrated on maintenance (29% of all AI implementations) and quality (27%), as illustrated by the graphic above. The survey, conducted among the 75 largest companies by revenue in the automotive, industrial manufacturing, consumer products, and aerospace and defense sectors, highlights these trends.
AI-powered visual systems, combined with advanced sensors, can detect defects and deviations in real-time, often more accurately than human inspectors. These systems can quickly scan products, identifying even the most minor flaws that could lead to costly recalls or dissatisfied customers.
5. Digital Twins and Virtual Simulations
The concept of digital twins—virtual replicas of physical systems—is gaining increasing popularity in the manufacturing industry. According to a McKinsey survey, 86% of respondents across various sectors, including manufacturing, believe that digital twins are applicable to their organizations. Additionally, 44% of these respondents have already implemented digital twins, with another 15% planning to do so.
Digital twins are especially useful in addressing challenges such as material and labor constraints, supply chain shortages, and the need for enhanced manufacturing visibility. They enable manufacturers to make faster, smarter, and more cost-effective decisions.
By simulating various scenarios, manufacturers can identify inefficiencies, test new strategies, and make informed decisions without disrupting actual production. This not only reduces downtime but also improves overall productivity.
You can learn more about this topic in the article:
Simulators vs digital twins: How to choose the best solution for your project?
6. Sustainability Through AI Optimization
Sustainability is a growing priority in manufacturing, and artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in helping companies achieve their environmental goals. AI is being used for various purposes, including:
- Optimizing energy consumption.
- Minimizing waste.
- Identifying inefficiencies in processes that consume excessive energy or generate unnecessary waste.
- Optimizing material use to reduce waste.
A notable example comes from a British company that provides AI-driven solutions to optimize energy consumption and generation. The client uses predictive models (machine learning) to optimize energy use, either to minimize costs or CO2 emissions, depending on their chosen target. AI helps them make optimal decisions about the energy produced and drawn from the power grid. This enables the client to pursue a zero-CO2 emissions strategy, where companies and communities can generate and use their own renewable energy. For more details, check out the article Utilizing Machine Learning (ML) in the optimization of energy use.
7. Strengthening Employee Capacity
While AI-based automation often sparks concerns about layoffs, the reality is that AI is more likely to enhance worker productivity rather than replace skilled professionals.
Current trends show that AI will increasingly be used to assist employees by providing real-time task insights, decision support, and automating repetitive tasks. For instance, AI systems can:
- Analyze production data to offer recommendations for process optimization.
- Alert employees to potential issues before they escalate.
- Simplify the control of complex machinery, requiring less specialized training.
Integrating AI into daily tasks will undoubtedly boost productivity and help build more tech-savvy teams.

Partnering with an Experienced AI Specialist in the Industry
As the manufacturing sector is in charge of digital transformation, artificial intelligence is becoming essential. From predictive maintenance to digital twins and quality control, AI is revolutionizing how manufacturers operate. Its application in these areas has a tremendous impact on process efficiency and safety.
To fully harness the potential of AI, manufacturers must take strategic, long-term action. This includes developing a comprehensive AI strategy that aligns with business objectives, investing in the required infrastructure, and fostering a culture of innovation.
If you’re interested in speaking with experienced experts in this field, please contact us. We will be happy to assess your organization’s needs and guide you in selecting the right technological solutions.