Table of Contents
What are feature toggles?
Feature toggles, also known as feature flags, are a technique that allows developers to turn certain features on or off in applications without having to implement new code. This can be illustrated with an example when you turn on a light in your house. You don’t have to change the house wiring every time. Use the switch, and you’re done. If you want to turn it off, press the switch again, and the light goes out. The same applies to feature flags; they allow you to release a new feature in your software or platform without downtime, so you can do it anytime, including during business hours. Such a toggle lets you dynamically choose a path in your code, whether building or running the product or in the execution environment. This highlights the use of “if” in code, which allows you to change the code’s behavior without rewriting it and processing everything in the deployment pipeline. At the same time, this technique will enable you to integrate your code much more frequently. It doesn’t require you to be stuck on your feature branch for weeks and wait until the feature is fully finished before integrating it with the rest of your code. You can merge unfinished functionality with the rest of the code, drop it into the “MAIN” – main branch of the version control, and put this unfinished code into production (of course, so as not to spoil this production ?).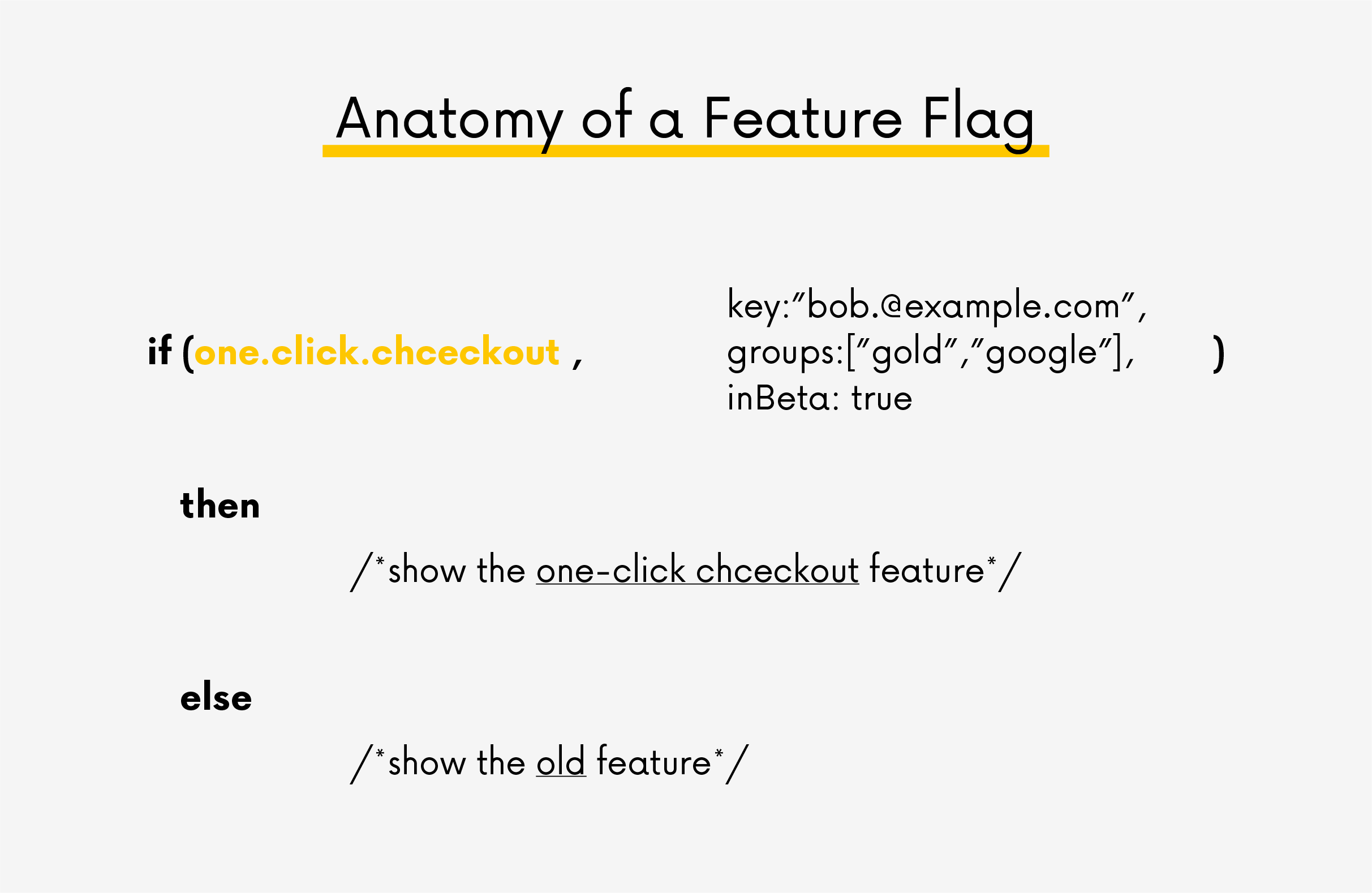
Advantages of feature flags
Feature flags allow teams to control feature releases, perform A/B testing, manage technical debt, and ensure smoother deployment. Here are the main advantages of feature flags in code: 1. Lower risk of implementation Function flags give a sense of psychological security. We know you can turn this flag off anytime, and this feature will not be seen. We gain the courage to integrate this code more often and gradually implement and experiment with different feature versions. 2. Faster software delivery The toggles allow new features to be tested in a production environment without making them available to all users, regardless of the main code base. 3. Get feedback faster With feature flags, it is possible to collect internal feedback from my company users and apply changes to unfinished functionality. 4. Improved development process Feature flags help segment users based on attributes, create and compare different feature variants, and measure their performance, helping optimize the user experience and business goals. 5. Controlling and monitoring Flags determine who can access features and collect feedback and data before making them available. It can also be used to gradually make features available to a subset of users and monitor their performance and impact. 6. Faster behavioral changes without requiring changes to the source code Feature toggles allow you to change the system’s behavior at any time. They may only require re-deployment, and even this step can be skipped if, for example, you use Spring Cloud Config, which allows you to change the application configuration without negatively affecting its availability.Types of feature flags and their purpose
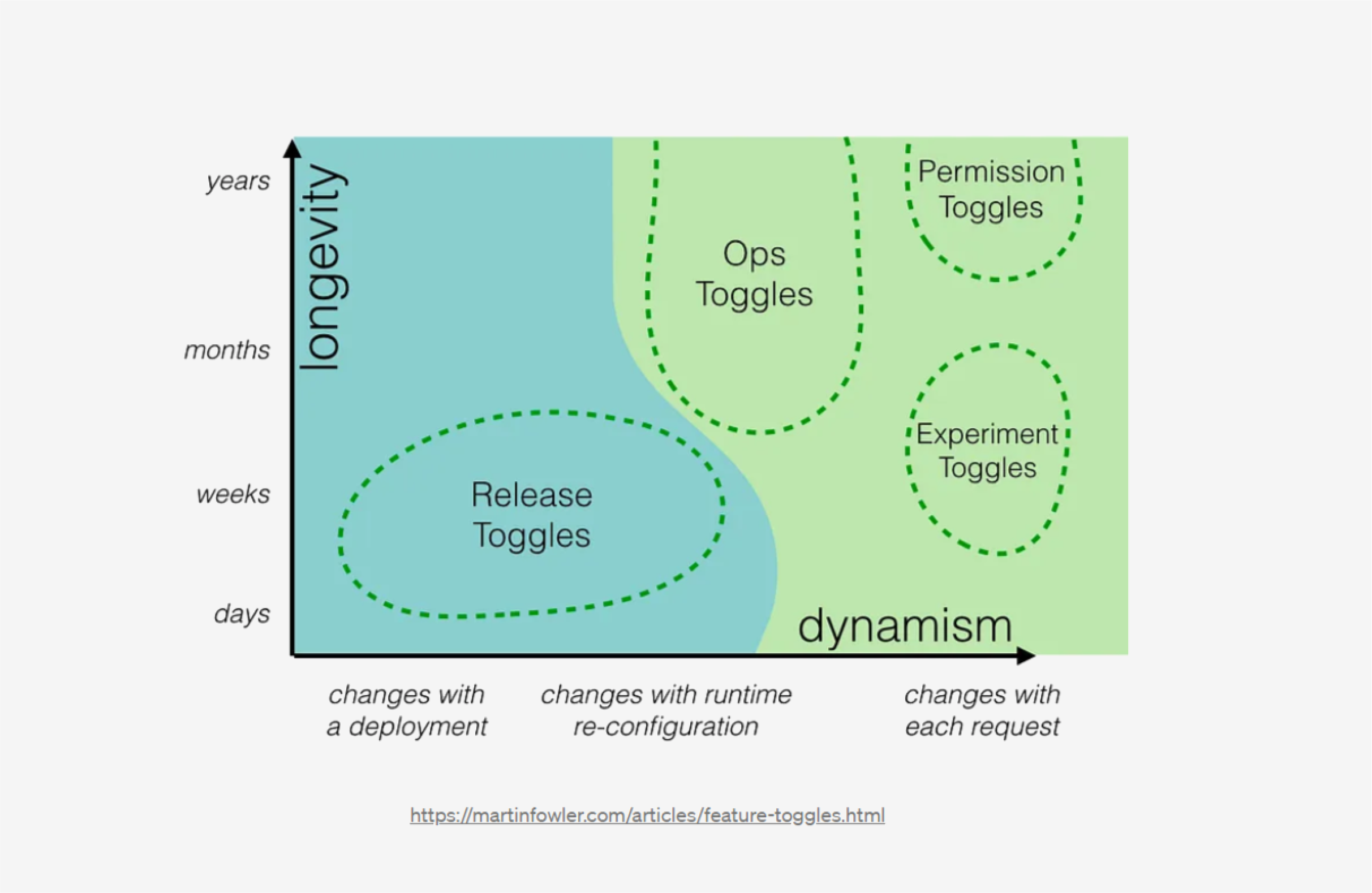
Feature flags, according to Martin Fowler, can be classified as follows:- Release toggles – These allow you to deploy code that has not yet been completed and hide incomplete features from users.
- Experiment toggles – This type is used in A/B testing. Such a flag often lives as long as we need to draw conclusions from the experiment results.
- Ops Toggles – Mainly used to control the operational aspects of the system by the people managing the application. They are typically used to disable specific toggles that are not necessary for the proper functioning of the application, for example, during heavy server load.
- Permission toggles – This type manages features available to different user groups. They are often used to manage premium and early access functionality.
Ways to implement feature flags
In Java, there are various approaches to implementing feature switching, including switches in a configuration file based on a database or using external services to manage them. Sometimes, there is an additional user interface application with a list of functions and a “switch” next to them. The function will be available in the target application if the flag is in the “on” position. Now we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of these approaches and when to use them.Configuration-based flags
This approach defines feature toggles in configuration files, such as properties, YAML, or JSON. The application reads these configuration files at runtime and enables or disables functions based on the values of the switches. Advantages:- The switches in the configuration file are easy to implement and understand.
- You can change the flags without modifying the code or reimplementing the application.
- Configuration files can be managed with version control systems, allowing tracking and auditing.
- Limited context awareness: Configuration-based switches typically do not support dynamic feature enablement based on user roles, permissions, or other contextual factors.
- As the number of features and switches increases, managing configuration files can become challenging.
Database-based feature flags
In this approach, feature toggles are stored and managed in a database or centralized configuration management system. The application queries the database or reads the configuration at runtime to determine which features should be enabled or disabled. Advantages:- You can modify toggles at runtime without restarting the application or changing the code.
- Context awareness: Toggles can be associated with user roles, permissions, or other contextual information stored in the database.
- Scalability: centralized storage allows feature flags to be managed across multiple instances or environments.
- Implementing feature flags requires additional infrastructure, such as a database or configuration management system.
- Frequent database queries can degrade performance, especially when evaluating toggles for each user request.
External tools for managing feature flags
Several solutions are available for managing feature flags. There are various SDK libraries available in Java that can be used to implement feature toggles. These libraries offer different features, integration options, and management capabilities. When choosing an SDK library for your Java project, consider factors such as: framework compatibility, function management requirements, ease of use and community support (to choose the one that best suits your needs). Some of the popular tools are: Togglz Pros:- Lightweight and easy to use
- Integrates well with Java EE and Spring frameworks
- Provides different strategies for activating function toggle
- Supports custom configuration options
- Active community support and regular updates
- Compared to other libraries, it has limited advanced feature management capabilities
- Limited support for remote management and configuration of feature flags
- Advanced feature management capabilities, including permission-based switching
- Seamless integration with Java frameworks such as Spring, CDI, and JAX-RS
- Provides a web console to manage feature flags
- Offers different activation and deactivation rules for switching functions
- Open-source software with an active community and regular updates
- Quite complicated documentation
- Not very flexible configuration options compared to other libraries
- Advanced feature toggles
- Multiple activation strategies and targeting options
- Centralized feature management server and dashboard
- Supports real-time configuration updates
- Good integration options and SDK support for Java
- Requires an external infrastructure or service to exploit its capabilities fully
- Comprehensive function management platform with powerful function-switching features
- Supports user-based targeting, A/B testing, and custom activation rules
- Has a web interface for managing feature flags and configurations
- Seamless integration with various development frameworks and services
- Provides extensive documentation and resources
- Requires subscription to access advanced features and full functionality
- Price may matter for small projects or startups
- Dependence on a third-party service to manage toggles
- Centralize locations to manage configuration properties, including feature switches. This makes updating and maintaining feature flags easier across multiple services or instances.
- Dynamic upgrades – Allow real-time modification of feature flag values without restarting or re-deploying the application. This flexibility allows for rapid experimentation and deployment of new features.
- Version control – In SCC, changes can be tracked, and previous versions restored if necessary, providing better control over configuration history.
- Security – Spring Cloud Config provides options for securing feature toggle properties through encryption and access control mechanisms. This guarantees protection against unauthorized access.
- Network dependency: If the configuration server is unavailable, the application may be unable to download updated feature toggles, potentially affecting system behavior.
- Increased complexity: Spring Cloud Config integration for feature flags adds a layer of complexity to the system architecture. It requires managing the configuration server, handling communication between the server and the application, and ensuring consistency between services.
Why separate the deployment from the release?
The conditional option “if” allows you to separate deployment from releasing because behind this “if” will be information about who will see the functionality and to whom it will be hidden. Why is it important to understand the difference between deployment and release of a project? The above two concepts differ. Deployment or implementation is – a technical event when we make changes to the software and move the code ultimately to the production environment; we can release this at any time. The release is exciting when these new features become available to end users. Here, feature flags allow us to control the release of this new feature on the deployment platform; that is, we choose who can see the latest versions of the software.In summary, feature toggles separate the two functions, we can deploy new software every day, but now we can decide to whom and when we show new versions.
Why are feature flags important in a continuous delivery and deployment mechanism?
Feature flagging enables efficient CI/CD, allowing developers to frequently merge their work into a shared repository without worrying about breaking anything or causing end users to access unfinished features. Flags give you control over the behavior of the application or platform, meaning that all code is always deployed. Still, some branches of code can be tested for new features, or you can disable it until the flag is turned on. Every time you enable a toggle, that code becomes available to users.Testing code equipped with feature flags
It depends on your testing strategy, whether it’s unit testing manual testing, etc. It is important not to test every possible combination of function flags but to run tests where there is a probability that something will happen. The test will also fail if the function is currently disabled. Therefore, removing the tests from the main process flow is best until the function is formally released. Until then, running tests only when required and if the function has been enabled is ideal. Once the function is finally released, the tests can be added to the main test run.What problems arise when we do not remove the flags?
The way function switches are managed shows the quality of the organization. Failure to remove function flags after their intended use can lead to several problems:- Technical debt – Feature flags left in the code base will accumulate over time, making the code base more complex and difficult to maintain, understand, and debug.
- Increased testing and maintenance effort – When feature flags are not removed, they are still part of the testing process, meaning that testers must test the associated code paths even if they are no longer relevant.
- Security risks – If unused and forgotten feature flags control access to sensitive functions or reveal unsecured functionality, they can be targeted if not properly secured.
- Performance degradation – Feature toggles often involve additional, conditional controls in the code. If these checks are not removed after the function is no longer needed, they can slow down the application.
- Compatibility issues – Feature flags can interact with other parts of the code base, dependencies, or integrations. Unused function flags can cause conflicts with other codes or introduce unintended behavior.